
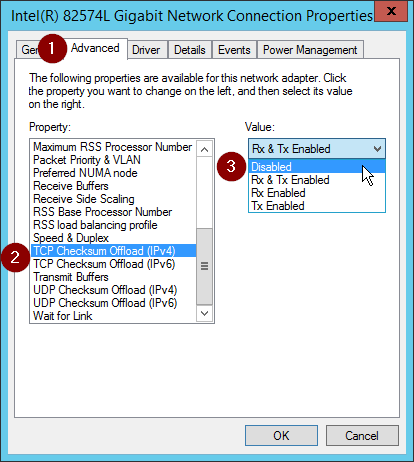
#Disable udp checksum offload windows vista keygen
When a TCP segment is lost, TCP assumes that the segment was lost due to congestion at a router and performs congestion control, which dramatically lowers the TCP sender’s transmission rate. You can enable CTCP with the netsh interface tcp set global congestionprovider=ctcp command and disable CTCP with the netsh interface tcp set global congestionprovider=none command. By working together, they can increase link utilization and produce substantial performance gains for large bandwidth-delay product connections.ĬTCP is enabled by default for computers running Windows Server 2008 and disabled by default for computers running Windows Vista.
Receive Window Auto Tuning optimizes receiver-side throughput and CTCP optimizes sender-side throughput. Connections with a larger bandwidth-delay product can have even better performance. In testing performed internally at Microsoft, large file backup times were reduced by almost half for a 1 Gigabit per second connection with a 50 millisecond round-trip time. CTCP also ensures that its behavior does not negatively impact other TCP connections. Compound TCPįor TCP connections with a large receive window size and a large bandwidth-delay product, Compound TCP (CTCP) in the Next Generation TCP/IP stack aggressively increases the amount of data sent at a time by monitoring the bandwidth-delay product, delay variations, and packet losses.
For more information, see “Quality of Service” in this article.įor more information about Receive Window Auto-Tuning, see Performance Enhancements in the Next Generation TCP/IP Stack and TCP Receive Window Auto-Tuning. If all the applications are optimized to receive TCP data, then the overall utilization of the network can increase substantially, making the use of Quality of Service (QoS) more important for networks that are operating at or near capacity. With better throughput between TCP peers, the utilization of network bandwidth increases during data transfer. Receive Window Auto-Tuning continually determines the optimal receive window size on a per-connection basis by measuring the bandwidth-delay product (the bandwidth multiplied by the latency of the connection) and the application retrieve rate, and automatically adjusts the maximum receive window size on an ongoing basis. To correctly determine the value of the maximum receive window size for a connection based on the current conditions of the network, the Next Generation TCP/IP stack supports Receive Window Auto-Tuning. The TCP receive window size is the amount of data that a TCP receiver allows a TCP sender to send before having to wait for an acknowledgement. The Next Generation TCP/IP stack is a complete redesign of TCP/IP functionality for both Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) that meets the connectivity and performance needs of today’s varied networking environments and technologies.įor a complete list of resources, see the Next Generation TCP/IP Stack Web page. Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista include a new implementation of the TCP/IP protocol stack known as the Next Generation TCP/IP stack. Internet Protocol security (IPsec) improvements.Windows Peer-to-Peer Networking enhancements.Network Device Interface Specification (NDIS) 6.0 and 6.1.Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista include many changes and enhancements to the following protocols and core networking components: With Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, IT administrators have greater and more flexible options for managing networking infrastructure, protecting their networks by requiring computers to prove their system health, deploying settings for authenticated wireless and wired connections through Group Policy or scripts, and deploying protected traffic scenarios. This article is a technical overview of networking and communications enhancements in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista to address connectivity, ease of use, management, reliability, and security. Partners, vendors, and others outside the network need to interact efficiently with key resources, and security is more important than ever. Employees need to connect to the network wherever they are and from any device. Networking and communications are critical for organizations to meet the challenge of competing in the global marketplace.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
